Gallstones, also known as biliary stones, are small solid particles that develop inside the gallbladder. They range in size—from tiny grains like sand to larger stones that may trigger significant pain.
These stones often go unnoticed, but if they block bile ducts, they can lead to sudden, intense discomfort along with several unpleasant symptoms.
Gallstones affect women more frequently, especially those with certain risk factors like a high-fat diet and a sedentary lifestyle. That’s why understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments is key to avoiding complications.
What Are Gallstones?
Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder — a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver that stores bile, a fluid involved in digesting fats.
As noted by the Cleveland Clinic, these stones are mainly made of cholesterol or bilirubin. While they often cause no noticeable symptoms, a blockage in the bile duct can lead to severe pain and inflammation (a condition known as cholelithiasis) that may require medical care.
There are two primary types of gallstones: cholesterol stones, the most common kind, and pigment stones, which develop due to high levels of bilirubin. Both types can disrupt bile flow and result in pain.
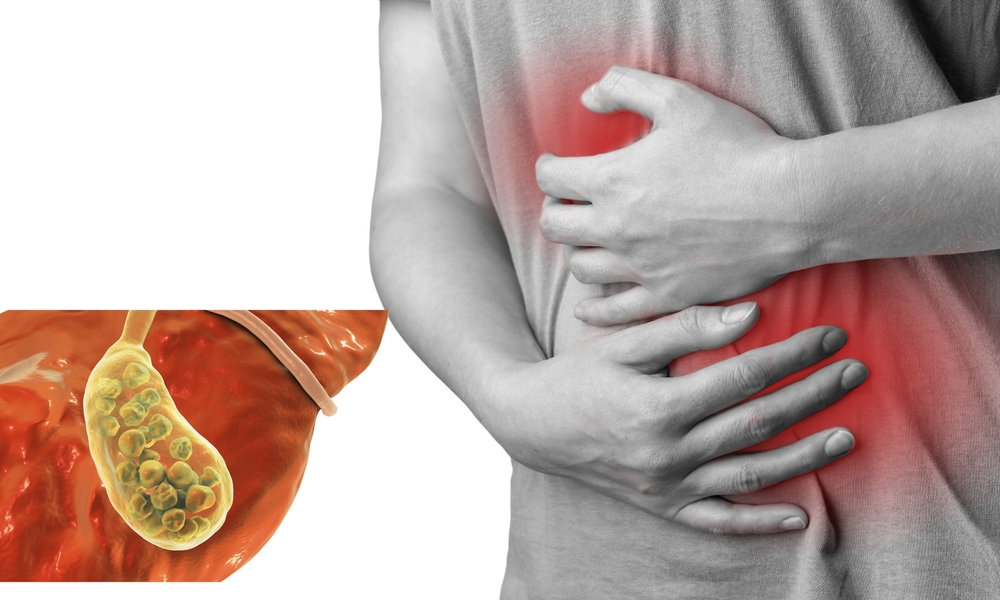
Symptoms of Gallstones
According to the Mayo Clinic, symptoms can vary based on the stone’s size and where it’s located. Common signs include:
- Intense pain in the upper right abdomen
- Discomfort in the mid-abdomen, beneath the breastbone
- Pain between the shoulder blades
- Pain in the right shoulder
- Nausea or vomiting
These symptoms often appear abruptly and may last anywhere from minutes to hours. In some cases, complications like infection or severe inflammation occur and need urgent medical treatment.
Causes of Gallstones
Gallstones form when there’s an imbalance in the bile’s components. As outlined by the BVSMS portal, key risk factors include:
- Diet high in fat and low in fiber
- Lack of physical activity and elevated LDL cholesterol
- Obesity and diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Smoking
- Long-term use of birth control pills
- Increased estrogen levels, more common in women
- Family history of gallstones
Living a healthy lifestyle with a good diet and regular exercise can help lower your risk.
Treatment for Gallstones
Treatment depends on how severe the symptoms are. The Cleveland Clinic recommends gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) as the most effective solution when bile ducts are blocked.
For those who cannot undergo surgery, alternatives include medications to dissolve the stones or non-invasive methods—though these may not eliminate all the stones.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical help if you have strong abdominal pain, especially if it’s accompanied by nausea or vomiting. Persistent or worsening symptoms could signal a bile duct obstruction. Fever and chills might suggest infection and require urgent evaluation.
Prevention Tips
To prevent gallstones, adopt healthy routines:
- Eat a diet rich in fiber and low in unhealthy fats
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid smoking
- Get regular check-ups to monitor risk factors
If something feels off, consult your healthcare provider. Staying proactive about your health can make all the difference.

















